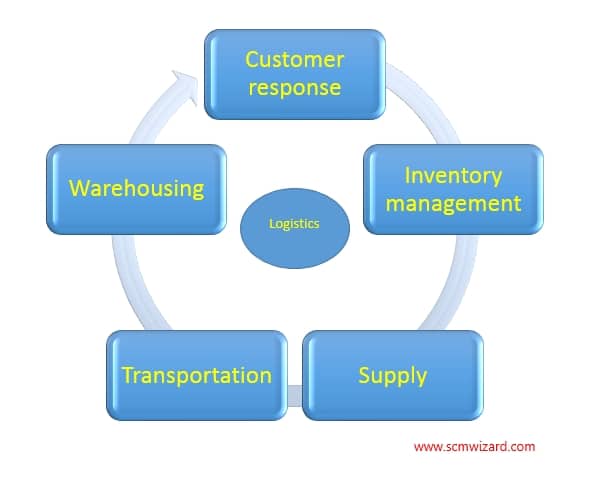
In our definition, logistics is comprised of five interdependent activities: customer response, inventory planning and management, supply, transportation, and warehousing. Each activity and its objective are described briefly in figure below and in detail here:
Read also: Concept of Logistics
Customer response:
Customer response links logistics externally to the customer base and internally to sales and marketing. Customer response is optimized when the customer service policy (CSP) yielding the lowest cost of lost sales, inventory carrying, and distribution is identified and executed.
The logistics of customer response includes the activities of:
- The logistics of customer response includes the activities of:
- Developing and maintaining a customer service policy
- Monitoring customer satisfaction
- Order entry (OE)
- Order processing (OP)
- Invoicing and collections
Inventory planning and management:
The objective of Inventory Planning and Management (IP&M) is to determine and maintain the lowest inventory levels possible that will meet the customer service policy requirements stipulated in the customer service policy. The logistics of inventory planning and management includes:
- Forecasting
- Order quantity engineering
- Service level optimization
- Replenishment planning
- Inventory deployment
Read also: Objectives of Logistics Management
Supply:
Supply is the process of building inventory (through manufacturing and/or procurement) to the targets established in inventory planning. The objective of supply management is to minimize the Total Acquisition Cost (TAC) while meeting the availability response time, and quality requirement stipulated in the customer service policy and the inventory master plan. The logistics of supply include:
- Developing and maintaining a Supplier Service Policy (SSP)
- Sourcing
- Supplier integration
- Purchase order processing
- Buying and payment
Transportation:
Transportation physically links the sources of supply chosen in sourcing with the customers we have decided to serve chosen as a part of the customer service policy. We reserve transportation for the fourth spot in the logistics activity list because the deliver-to points and response time requirements determined in the customer service policy and the pick-up points determined in the supply plan must be in place before a transportation scheme can be developed.
Read also: Basic cost elements in transportation
The objective of transportation is to link all pick-up and deliver-to points within the response time requirements of the customer service policy and the limitations of the transportation infrastructure at the lowest possible cost. The logistics of transportation includes:
- Network design and optimization
- Shipment management
- Fleet and container management
- Carrier management
- Freight management
Read also: Concept of Logistics
Warehousing
I present warehousing as the last of the five logistics activities because good planning in the other four may eliminate the need for the warehousing or may suggest the warehousing activity be outsourced. In addition, a good warehouse plan incorporates the needs of all the other logistics activities. Good or bad, the warehouse ultimately portrays the efficiency or inefficiency of the entire supply chain.
Read also: Concept of Warehouse
The objective of warehousing is to minimize the cost of labor, space, and equipment in the warehouse while meeting the cycle time and shipping accuracy requirements of the customer service policy and the storage capacity requirements of the inventory play. The logistics activities of warehousing includes:
- Receiving
- Put away
- Storage
- Order picking
- Shipping
Reference:
Frazelle, Edward. Supply Chain Strategy. McGraw-Hill, 2002. https://books.google.com/






need more flesh in the article
Thanks for your comment. We’ll publish more article about logistics activities soon. keep in touch.