When it comes to the discussion of the letter of credit, then obviously you have to know about UPAS LC.
This is a solution for both buyer and seller for the credit and payment problems.
Here I’ll explain the A-Z of UPAS LC which you may not find anywhere. This is based on practical examples and experience.
Definition
UPAS LC is Usance Payable at Sight. From the name, you understand that it is the combination of Usance LC and Sight LC.
In UPAS LC the seller (Beneficiary) receives the payment at sight basis but the buyer (Applicant) enjoys the Usance facility.
Note: If the payment term is deferred, then the beneficiary will receive payment after the deferred period, and then discounting period will start.
The Usance funding is provided by the bank to the applicant. It may be the OBU of issuing bank or advising bank or any third bank that does the discounting (discounting bank).
UPAS period
It depends upon the arrangement between the buyer (applicant) and his bank (issuing bank). But for raw materials, it could be up to 180 days (in some cases 360 days) and for capital machinery, it could extend up to 360/720days.
Discounting rate/interest
Based on the UPAS tenor the discounting bank will provide the discounting rate. There are some other issues that also depend on discounting such as applicant’s status/credibility, issuing bank status/credibility, items in PI, credit line with the issuing bank, etc. as per compliance of the discounting bank.
Some banks provide a flat rate such as 4%~6%. But in general, it is offered by a formula with the Libor rate. Such as L+2%. It may include confirmation costs.
Here 2%/4%/6% I’ve mentioned above is just for example.
Note: Discounting interest start from the day discounting bank makes payment to the seller’s bank.
UPAS process
Photo credit: https://international.groupecreditagricole.com/
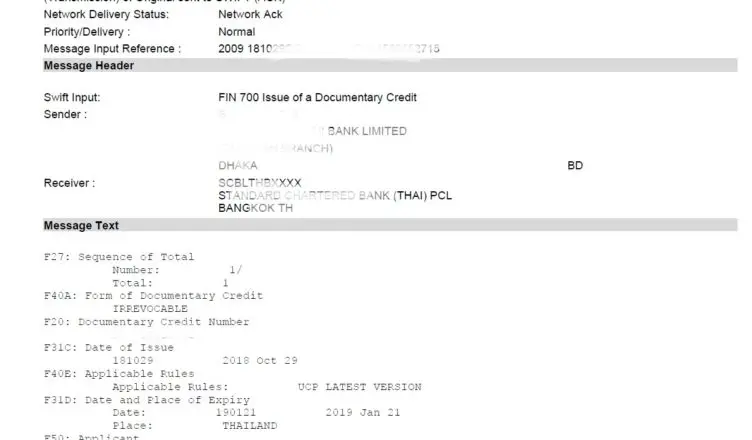
First Based on agreed terms and conditions buyer (applicant) opens LC through issuing bank. These LC clauses should include the terms and conditions of UPAS. This is like regular import LC but some payment terms, instructions, and presentation is different. I’ll explain with an example in the example section.
Secondly, the supplier (beneficiary) makes the shipment of goods and presents the documents to the advising bank. Advising bank sends documents to discounting bank. Discounting bank checks and if comply then they can make payment to the supplier. It depends upon the instruction in the LC. The discounting sends the documents to the issuing bank and may wait for their confirmation/authorization to make the payment to the supplier.
Thirdly, after the UPAS period, the discounting bank claims payment from the issuing bank. The issuing bank collects payment from the applicant and made payment to the discounting bank.
If the applicant makes a delay in the payment in the stipulated period, then issuing bank may make payment to the discounting bank and make a forced loan to the applicant. It depends upon the arrangement between the applicant and the issuing bank.
There’s another stage that remains most of the time in UPAS LC which is “confirmation”. Discounting bank requests for confirmation and even suppliers ask for confirmation in the LC. In this case “confirming bank” takes the responsibility for the payment if the buyer/issuing bank made a delay for the payment. So, a confirmation charge is added to the LC. This charge may bear either by the applicant or by the beneficiary based on their negotiation.
Parties involved
From the above discussion, you have already found several parties involved in UPAS LC. I’ll describe them shortly for your understanding:
Applicant: The buyer who opens the LC is the applicant (F50 in LC).
Beneficiary: The seller who receives the LC is the Beneficiary (F59 in LC).
Issuing bank: The LC opening bank is the issuing bank/applicant bank (if this bank issues LC)/opening bank.
Advising bank: The bank that advises the LC to the beneficiary.
Negotiating bank: In this bank seller make the presentation for payment. Negotiating bank may be the same bank as advising bank and discounting bank.
Discounting bank: This bank provides funding for the UPAS.
OBU: This is the Offshore-Banking Unit of the local bank (LC issuing bank). They can do the discounting. They maintain a foreign account and arrange payments in foreign currency.
Confirming bank: The bank that adds confirmation in the LC. They will take confirmation charge. It may be the advising bank or discounting bank or OBU.
Reimbursing Bank: This bank makes payment to the nominated bank (here discounting bank) on behalf of the issuing bank. This is situated in a foreign country and have NOSTRO account with issuing bank as because the local bank cannot make foreign currency payment directly.
Example
Let’s analyze a real UPAS LC and what’s the term and conditions mentioned.

The LC should be received by discounting bank. You cannot send LC to the beneficiary bank directly. Here’s Wells Fargo SG is the discounting bank. Beneficiary bank is different. Wells Fargo SG will advise this LC to the beneficiary bank.

In F41A (Available With… By… Identifier code) the discounting bank is mentioned. If it’s normal sight LC then it can be “any bank of the country”. But in UPAS LC the documents should be sent to the discounting bank counter.
In F42C (Drafts at…) the UPAS period is mentioned. Here you can see the beneficiary will get payment at 30 days from B/L. It’s determined by the negotiation between buyer and seller.
But the 180days mentioned here, is not the issue of the seller. It’s the arrangement of the UPAS period by the buyer.

In F47A (additional conditions) here it’s also mentioned that the beneficiary will be paid at 30days B/L by the discounting bank.

Here in F47A (Additional conditions) clause 21 is related to the charges. Who will bear the discounting interest is based on the negotiation between buyer and seller. From F71D (Charges) this clause is referred.
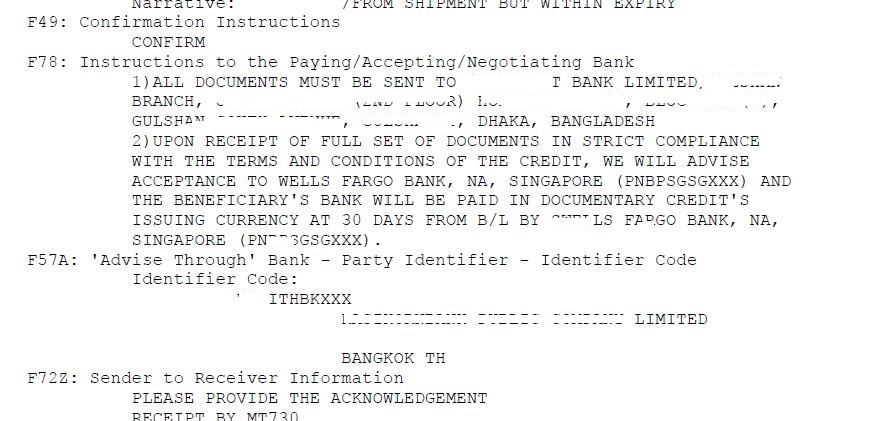
F49 (Confirmation Instructions) is “CONFIRM” which means this is a confirmed LC. UPAS LC may be without add confirmation. But confirmation is requested by the seller or discounting bank as they have to keep the limit.
In F78 (Instructions to the Paying/Accepting/Negotiating bank) you can see the instruction for the payment is mentioned here.
F57A (Advise through bank) is the beneficiary bank.
Benefit of buyer
UPAS LC provides some benefits to the buyer.
Increase negotiation power to the buyer as the seller receive payment immediately after shipment/presentation.
The interest rate is much lower than any other method. Financing is done from the foreign banks where the interest rate is much lower than in our country.
It helps to get additional credit for the buyer. So it optimizes the working capital.
Benefit of seller
UPAS LC also provides some advantages to the seller.
Seller receives payment immediately after presentation and acceptance.
They are assured about payment through confirmed LC.
Their cash flow is good as they don’t have to extend the credit period.
What is the difference between sight LC and UPAS LC
At sight LC the supplier receives the payment at sight basis.
In UPAS LC the supplier can receive the payment at sight basis.
But the difference is, in UPAS LC the buyer gets the extra Usance period to make the payment whereas in sight LC the buyer has to make payment at documents acceptance.
UPAS LC refinancing
This is an additional topic for your knowledge. There’s another option for refinancing UPAS LC. That means during the maturity of discounting period the buyer can increase the Usance period by arranging refinance from the bank. This provides an additional deferred payment facility for the buyer.
I hope you will now have a clear understanding of UPAS LC. If there anything to add you can share it with us.